Understanding Human-Like Robotics
Human-like robotics is a fascinating field that combines various elements from engineering, computer science, and design. Over the years, the development of humanoid robots has progressed significantly, transitioning from simple mechanical devices to complex, intelligent beings that are often referred to as Human Like Robots. These robots mimic human movements and behaviors, making them relatable and capable of performing tasks that require a human-like presence. But what do we really know about the evolution of these fascinating machines? Understanding their history provides key insights into their current capabilities and future potential.
The evolution of humanoid robots began in ancient times, when inventors dreamed of creating machines that could resemble humans. It saw an acceleration during the 20th century with advancements in electronics and computing. Today, these robots are equipped with sensors and AI, enabling them to interact with their environment effectively. They not only serve in commercial settings—like hospitality and healthcare—but are also becoming common in homes. As technology improves, we continue to see new features and functionalities integrated into these fascinating creations.
Conceptualizing Your Custom Robot Design
When working on a custom robot project, the first step is often to identify the purpose your robot will serve. Is it meant for companionship, assistance, entertainment, or perhaps education? A clear understanding of its function will guide many decisions throughout the design and building process. Without a set purpose, the design can become confusing and inefficient. By thoughtfully defining its role, you lay a strong foundation for further development.
Establishing design specifications includes considerations about size, weight, and capabilities. You’ll want to think about how the robot will navigate its environment and the specific tasks it needs to accomplish. Additionally, it’s crucial to determine the materials needed for construction, as they will affect the robot’s performance and durability. These specifications also help to identify the technological components required, such as sensors and processors. Keep in mind that these specifications will evolve as you gain more insights during the development process.
Engineering the Structure of the Robot
Once you’ve conceptualized your robot, the next phase is engineering its structure. Material selection is vital as it affects not only the robot’s longevity but also its flexibility and range of movements. Commonly used materials include lightweight metals, plastics, and composites, which can provide both strength and agility. It's important to consider how these materials will interact with the robot's electronic components. A well-engineered framework is essential for supporting all parts and allowing movement.
Building the skeletal framework involves creating a robust internal structure that can support the external features. This framework often resembles a human skeleton, with joints simulating human movement. Designing joints and motors for movement is another crucial aspect; it allows the robot to perform activities similar to humans, such as walking and grasping objects. Choosing the right types of actuators will affect the smoothness and realism of these movements, and integrating these systems correctly is vital for overall functionality.
Addressing Robotics Software and Programming
Software development is just as important as physical engineering when it comes to creating a functional robot. Understanding control systems and algorithms helps clarify how the various components will interact. Control systems manage the robot's movements, allowing it to respond to commands and navigate effectively. Developing these systems requires a solid grasp of coding and robotics principles. Do you have the right programming skills for this part of the project? It might be worth considering collaboration with experts in the field.
Implementing artificial intelligence can take your robot's capabilities to new heights. AI facilitates autonomy, enabling the robot to make decisions based on sensory data. This autonomy allows for more interactive and engaging user experiences. Additionally, many modern humanoid robots incorporate sensory systems, which provide feedback mechanisms critical to understanding the environment. Proper integration of these systems ensures your robot can adapt to various situations, enhancing its functionality.
Creating the Interactive Interface
The interactive interface of a humanoid robot greatly affects user experience. Designing user interaction techniques is essential for creating an intuitive relationship between the robot and users. Will the robot respond to touch, gestures, or voice commands? You must consider what methods will be most effective for communication. Engaging interaction encourages users to develop a bond with the robot, making it more appealing and useful in various contexts.
Voice recognition and natural language processing are key features for a well-functioning interactive interface. These technologies allow the robot to understand and respond to verbal commands, making it feel more like a natural conversation. Such capabilities can enhance user experience significantly, as they minimize the barriers to communication. An intuitive user interface also involves considering visual and tactile interactions, ensuring that the robot provides feedback in a way that users can easily comprehend and respond to.
Enhancing Realism and Visual Appearance
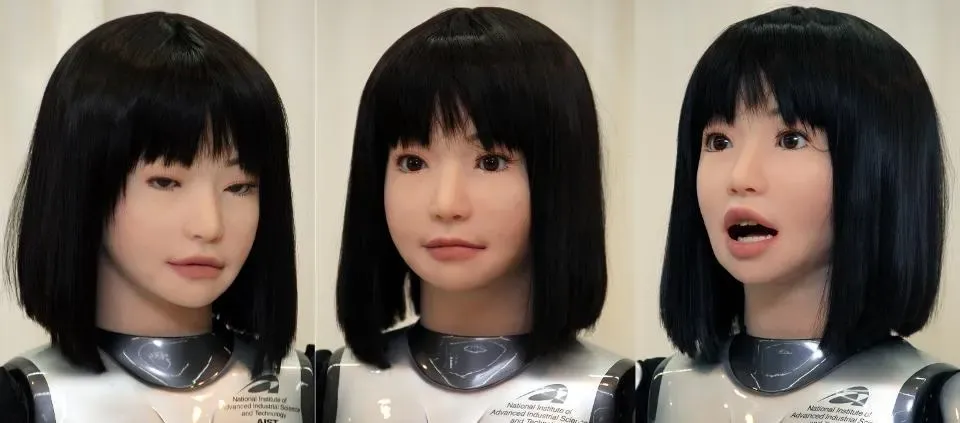
Realism plays a significant role in the success of a humanoid robot. Crafting realistic facial features and expressions enhances relatability, helping users feel more comfortable. Consider techniques like 3D printing, which allows for precise detailing in facial structures. Subtle expressions can give the robot a more lively appearance, drawing users in and promoting interaction. Remember, the more lifelike your robot appears, the more likely users are to engage it.
Selecting the right skin materials adds another layer of realism. Silicones and elastomers that mimic human skin texture can greatly improve the visual and tactile appeal of the robot. These materials must not only look realistic but also be durable enough to withstand wear and tear. Additionally, incorporating hair, clothing, or other aesthetic features can elevate the robot's attractiveness. Users naturally gravitate toward familiar qualities, so the more you can replicate human appearance, the more successful your design is likely to be.
Testing and Iteration in Robot Development
Once construction is complete, testing your robot is crucial. Establishing testing protocols ensures that your robot performs efficiently in real-world situations. Consider factors such as movement accuracy, interaction quality, and system reliability. The objective is to identify any flaws or limitations in the design and functionality. Conducting thorough tests will provide insights into areas that require improvement.
Safety considerations should also be a part of the testing phase. Ensuring that the robot operates safely around people and other objects is paramount. You must also implement risk management strategies to mitigate potential hazards. Utilizing feedback for design improvements creates a loop where every piece of information can help refine the robot's functionality further. Iterative testing ensures that your final product is well-equipped to meet user needs.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
As humanoid robots become more prevalent, ethical and regulatory considerations gain importance. Addressing privacy and security concerns is essential, as these robots often interact closely with humans. Questions around data protection and personal information should be at the forefront of the design process. Compliance with ethical standards can affect the robot's acceptance in society and its overall success.
It's equally important to think about the ethical use of human-like robots. For instance, issues related to labor, companionship, and potentially replacing human roles must be considered. Striking a balance between beneficial use and ethical implications can be challenging but necessary. Additionally, navigating regulatory compliance ensures that the robot adheres to established laws and standards. This compliance contributes to safer and more effective robot designs overall.
Future Directions in Humanoid Robotic Design
As technology continues to advance, the future of humanoid robot design looks promising. Innovations in robotics hardware and software are leading to more sophisticated and capable machines. We can expect improvements in cost-effectiveness and accessibility, making custom robots attainable for a broader audience. These innovations open up new horizons for experimentation and development in this exciting field.
Potential applications for human-like robots are limitless. From enhancing healthcare with compassionate companions to revolutionizing customer service, the possibilities are vast. As industries adopt these technologies, opportunities for market growth and demand will increase. Furthermore, long-term implications on society could reshape our understanding of relationships and interactions. As humanoid robots evolve, they may not only assist us but also become integral parts of our daily lives.